- Home
- About Us
- TSPT Academy
- Online Courses
-
Resources
- Newsletter
- Business Minded Sports Physio Podcast
- Day in the Life of a Sports PT
- Residency Corner
-
Special Tests
>
-
Cervical Spine
>
- Alar Ligament Test
- Bakody's Sign
- Cervical Distraction Test
- Cervical Rotation Lateral Flexion Test
- Craniocervical Flexion Test (CCFT)
- Deep Neck Flexor Endurance Test
- Posterior-Anterior Segmental Mobility
- Segmental Mobility
- Sharp-Purser Test
- Spurling's Maneuver
- Transverse Ligament Test
- ULNT - Median
- ULNT - Radial
- ULNT - Ulnar
- Vertebral Artery Test
- Thoracic Spine >
-
Lumbar Spine/Sacroiliac Joint
>
- Active Sit-Up Test
- Alternate Gillet Test
- Crossed Straight Leg Raise Test
- Extensor Endurance Test
- FABER Test
- Fortin's Sign
- Gaenslen Test
- Gillet Test
- Gower's Sign
- Lumbar Quadrant Test
- POSH Test
- Posteroanterior Mobility
- Prone Knee Bend Test
- Prone Instability Test
- Resisted Abduction Test
- Sacral Clearing Test
- Seated Forward Flexion Test
- SIJ Compression/Distraction Test
- Slump Test
- Sphinx Test
- Spine Rotators & Multifidus Test
- Squish Test
- Standing Forward Flexion Test
- Straight Leg Raise Test
- Supine to Long Sit Test
-
Shoulder
>
- Active Compression Test
- Anterior Apprehension
- Biceps Load Test II
- Drop Arm Sign
- External Rotation Lag Sign
- Hawkins-Kennedy Impingement Sign
- Horizontal Adduction Test
- Internal Rotation Lag Sign
- Jobe Test
- Ludington's Test
- Neer Test
- Painful Arc Sign
- Pronated Load Test
- Resisted Supination External Rotation Test
- Speed's Test
- Posterior Apprehension
- Sulcus Sign
- Thoracic Outlet Tests >
- Yergason's Test
- Elbow >
- Wrist/Hand >
- Hip >
- Knee >
- Foot/Ankle >
-
Cervical Spine
>
- I want Financial Freedom
- I want Professional Growth
- I want Clinical Mastery
Percussion Test
Purpose: To assess for a fracture in the lower extremity.
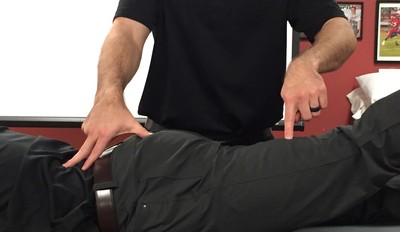
Test Position: Supine.
Performing the Test: The patient should not be wearing shoes. The examiner then strikes the heel of the patient. A positive test is reproduction of the patient's worst pain.
Diagnostic Accuracy: Unknown.
Importance of Test: Our bones are covered by a layer of tissue known as the periosteum. It is highly innervated and very sensitive to injury. When a bone is fractured, the periosteum is more easily stimulated and thus pain is experienced. By striking the heel of the foot, a large vibratory/compression force is sent through the limb that stimulates the injured site. It should be noted that the percussion test can produce pain in non-musuloskeletal ailments as well, such as psoas abscess, appendicitis, etc. It is important to utilize your subjective history, tests and measures, and general systems screenings to triangulate your findings.
Note: these tests should only be used by properly trained health care practitioners.
Test Position: Supine.
Performing the Test: The patient should not be wearing shoes. The examiner then strikes the heel of the patient. A positive test is reproduction of the patient's worst pain.
Diagnostic Accuracy: Unknown.
Importance of Test: Our bones are covered by a layer of tissue known as the periosteum. It is highly innervated and very sensitive to injury. When a bone is fractured, the periosteum is more easily stimulated and thus pain is experienced. By striking the heel of the foot, a large vibratory/compression force is sent through the limb that stimulates the injured site. It should be noted that the percussion test can produce pain in non-musuloskeletal ailments as well, such as psoas abscess, appendicitis, etc. It is important to utilize your subjective history, tests and measures, and general systems screenings to triangulate your findings.
Note: these tests should only be used by properly trained health care practitioners.
Copyright © The Student Physical Therapist LLC 2023