- Home
- About Us
- TSPT Academy
- Online Courses
-
Resources
- Newsletter
- Business Minded Sports Physio Podcast
- Day in the Life of a Sports PT
- Residency Corner
-
Special Tests
>
-
Cervical Spine
>
- Alar Ligament Test
- Bakody's Sign
- Cervical Distraction Test
- Cervical Rotation Lateral Flexion Test
- Craniocervical Flexion Test (CCFT)
- Deep Neck Flexor Endurance Test
- Posterior-Anterior Segmental Mobility
- Segmental Mobility
- Sharp-Purser Test
- Spurling's Maneuver
- Transverse Ligament Test
- ULNT - Median
- ULNT - Radial
- ULNT - Ulnar
- Vertebral Artery Test
- Thoracic Spine >
-
Lumbar Spine/Sacroiliac Joint
>
- Active Sit-Up Test
- Alternate Gillet Test
- Crossed Straight Leg Raise Test
- Extensor Endurance Test
- FABER Test
- Fortin's Sign
- Gaenslen Test
- Gillet Test
- Gower's Sign
- Lumbar Quadrant Test
- POSH Test
- Posteroanterior Mobility
- Prone Knee Bend Test
- Prone Instability Test
- Resisted Abduction Test
- Sacral Clearing Test
- Seated Forward Flexion Test
- SIJ Compression/Distraction Test
- Slump Test
- Sphinx Test
- Spine Rotators & Multifidus Test
- Squish Test
- Standing Forward Flexion Test
- Straight Leg Raise Test
- Supine to Long Sit Test
-
Shoulder
>
- Active Compression Test
- Anterior Apprehension
- Biceps Load Test II
- Drop Arm Sign
- External Rotation Lag Sign
- Hawkins-Kennedy Impingement Sign
- Horizontal Adduction Test
- Internal Rotation Lag Sign
- Jobe Test
- Ludington's Test
- Neer Test
- Painful Arc Sign
- Pronated Load Test
- Resisted Supination External Rotation Test
- Speed's Test
- Posterior Apprehension
- Sulcus Sign
- Thoracic Outlet Tests >
- Yergason's Test
- Elbow >
- Wrist/Hand >
- Hip >
- Knee >
- Foot/Ankle >
-
Cervical Spine
>
- I want Financial Freedom
- I want Professional Growth
- I want Clinical Mastery
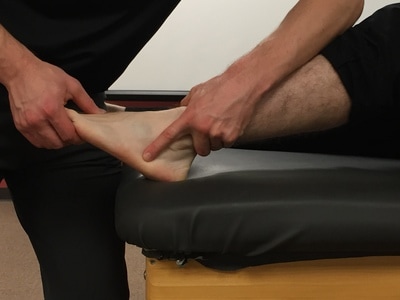
Test for Interdigital Neuroma
Purpose: To test for the presence of a neuroma.
Test Position: Supine.
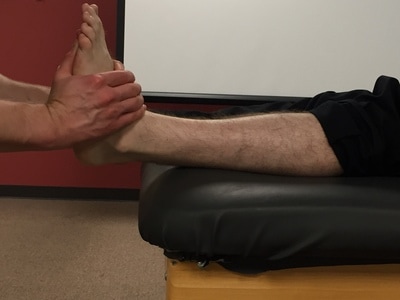
Performing the Test: Grasp the metatarsal bones of the two metatarsal between which is the suspected neuroma. Next, the examiner moves the metatarsal back and forth while compressing them. A positive test is reproduction of the patient's symptoms. Often these symptoms are described as shooting, burning, or tingling pains.
Diagnostic Accuracy: Unknown.
Importance of Test: Morton's neuroma is an entrapment neuroma of the interdigital plantar nerve. It is more common in women between the fifth and sixth decades. Additionally, the third inter-metatarsal space is most commonly involved. Because the neuroma is directly connected to the nervous system, irritating the neuroma will cause nervous type symptoms, specifically numbness, burning or shooting pain. By compressing the suspected metatarsals, the examiner is mimicking metatarsal movements that would happen during gait or with foot motion.
Note: these tests should only be performed by a properly trained health care practitioner.
Test Position: Supine.
Performing the Test: Grasp the metatarsal bones of the two metatarsal between which is the suspected neuroma. Next, the examiner moves the metatarsal back and forth while compressing them. A positive test is reproduction of the patient's symptoms. Often these symptoms are described as shooting, burning, or tingling pains.
Diagnostic Accuracy: Unknown.
Importance of Test: Morton's neuroma is an entrapment neuroma of the interdigital plantar nerve. It is more common in women between the fifth and sixth decades. Additionally, the third inter-metatarsal space is most commonly involved. Because the neuroma is directly connected to the nervous system, irritating the neuroma will cause nervous type symptoms, specifically numbness, burning or shooting pain. By compressing the suspected metatarsals, the examiner is mimicking metatarsal movements that would happen during gait or with foot motion.
Note: these tests should only be performed by a properly trained health care practitioner.
References:
Torres-Claramunt, R. "MRI and ultrasonography in Morton's neuroma: Diagnostic accuracy and correlation." Indian Journal of Orthopaedics . 45.May- June 2012 (2012): n. page. Web. 5 Oct.
Copyright © The Student Physical Therapist LLC 2023