- Home
- About Us
- TSPT Academy
- Online Courses
-
Resources
- Newsletter
- Business Minded Sports Physio Podcast
- Day in the Life of a Sports PT
- Residency Corner
-
Special Tests
>
-
Cervical Spine
>
- Alar Ligament Test
- Bakody's Sign
- Cervical Distraction Test
- Cervical Rotation Lateral Flexion Test
- Craniocervical Flexion Test (CCFT)
- Deep Neck Flexor Endurance Test
- Posterior-Anterior Segmental Mobility
- Segmental Mobility
- Sharp-Purser Test
- Spurling's Maneuver
- Transverse Ligament Test
- ULNT - Median
- ULNT - Radial
- ULNT - Ulnar
- Vertebral Artery Test
- Thoracic Spine >
-
Lumbar Spine/Sacroiliac Joint
>
- Active Sit-Up Test
- Alternate Gillet Test
- Crossed Straight Leg Raise Test
- Extensor Endurance Test
- FABER Test
- Fortin's Sign
- Gaenslen Test
- Gillet Test
- Gower's Sign
- Lumbar Quadrant Test
- POSH Test
- Posteroanterior Mobility
- Prone Knee Bend Test
- Prone Instability Test
- Resisted Abduction Test
- Sacral Clearing Test
- Seated Forward Flexion Test
- SIJ Compression/Distraction Test
- Slump Test
- Sphinx Test
- Spine Rotators & Multifidus Test
- Squish Test
- Standing Forward Flexion Test
- Straight Leg Raise Test
- Supine to Long Sit Test
-
Shoulder
>
- Active Compression Test
- Anterior Apprehension
- Biceps Load Test II
- Drop Arm Sign
- External Rotation Lag Sign
- Hawkins-Kennedy Impingement Sign
- Horizontal Adduction Test
- Internal Rotation Lag Sign
- Jobe Test
- Ludington's Test
- Neer Test
- Painful Arc Sign
- Pronated Load Test
- Resisted Supination External Rotation Test
- Speed's Test
- Posterior Apprehension
- Sulcus Sign
- Thoracic Outlet Tests >
- Yergason's Test
- Elbow >
- Wrist/Hand >
- Hip >
- Knee >
- Foot/Ankle >
-
Cervical Spine
>
- I want Financial Freedom
- I want Professional Growth
- I want Clinical Mastery
|
With the foot and ankle acting as a foundation for the human body, mobility limitations can impact how we move as a whole. Check out this complimentary video from Insider Access on manual treatment methods for improving talocrural mobility.
|
|
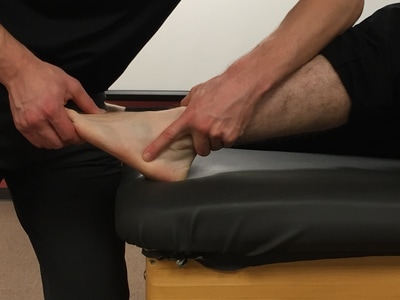
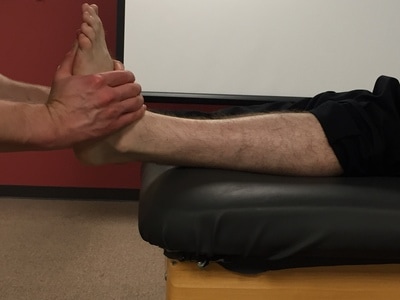
Talar Tilt
Purpose: To test for injury to the lateral ligaments of the ankle.
Test Position: Supine or sitting.
Performing the Test: The examiner stabilizes the distal leg in a neutral position and inverts the ankle. The examiner then determines how much inversion is present. The amount present is graded on a 4 point scale of 0-3, with 0 being no laxity and 3 being gross laxity. Flynn describes an alternate method of grading as <5 degrees, 5-15 degrees, or >15 degrees. Under anesthesia, >15 degrees was associated with complete rupture of both the anterior talofibular ligament and calcaneofibular ligament.
Diagnostic Accuracy: Unknown
Importance of Test: When assessing inversion and eversion motion at the ankle, you are describing motion that occurs parallel to the frontal plane (This motion is not to be confused with supination, which is a combination of inversion, adduction, and plantar flexion). By placing the patient in a position of inversion, you are stressing the lateral ligaments of the ankle. The degree to which lateral ligament is placed under the greatest stretch is debatable. An article written by Docherty et al believes that the calcaneofibular ligament is the primary ligament being stretched during the talar tilt test. This ligament courses from apex of the lateral malleolus inferiorly and posteriorly to the lateral calcaneus. During an inversion moment, a stress will be placed upon this ligament. If injury has occurred to the lateral ankle, the lateral ankle ligaments could be lax and increased inversion motion may be present.
Note: these tests should only be performed by properly trained health care practitioners
Test Position: Supine or sitting.
Performing the Test: The examiner stabilizes the distal leg in a neutral position and inverts the ankle. The examiner then determines how much inversion is present. The amount present is graded on a 4 point scale of 0-3, with 0 being no laxity and 3 being gross laxity. Flynn describes an alternate method of grading as <5 degrees, 5-15 degrees, or >15 degrees. Under anesthesia, >15 degrees was associated with complete rupture of both the anterior talofibular ligament and calcaneofibular ligament.
Diagnostic Accuracy: Unknown
Importance of Test: When assessing inversion and eversion motion at the ankle, you are describing motion that occurs parallel to the frontal plane (This motion is not to be confused with supination, which is a combination of inversion, adduction, and plantar flexion). By placing the patient in a position of inversion, you are stressing the lateral ligaments of the ankle. The degree to which lateral ligament is placed under the greatest stretch is debatable. An article written by Docherty et al believes that the calcaneofibular ligament is the primary ligament being stretched during the talar tilt test. This ligament courses from apex of the lateral malleolus inferiorly and posteriorly to the lateral calcaneus. During an inversion moment, a stress will be placed upon this ligament. If injury has occurred to the lateral ankle, the lateral ankle ligaments could be lax and increased inversion motion may be present.
Note: these tests should only be performed by properly trained health care practitioners
Reference: Flynn, Timothy. "Users Guide to the Musculoskeletal Examination."
Docherty, Carrie. "Reliability of the Anterior Drawer and Anterior Tilt Tests using the Ligmaster Joint Arthometer." 2009.
Neumann, Donald. Kinesiology of the Musculoskeletal System. 2nd Edition.
Docherty, Carrie. "Reliability of the Anterior Drawer and Anterior Tilt Tests using the Ligmaster Joint Arthometer." 2009.
Neumann, Donald. Kinesiology of the Musculoskeletal System. 2nd Edition.
Copyright © The Student Physical Therapist LLC 2023