- Home
- About Us
- TSPT Academy
- Online Courses
-
Resources
- Newsletter
- Business Minded Sports Physio Podcast
- Day in the Life of a Sports PT
- Residency Corner
-
Special Tests
>
-
Cervical Spine
>
- Alar Ligament Test
- Bakody's Sign
- Cervical Distraction Test
- Cervical Rotation Lateral Flexion Test
- Craniocervical Flexion Test (CCFT)
- Deep Neck Flexor Endurance Test
- Posterior-Anterior Segmental Mobility
- Segmental Mobility
- Sharp-Purser Test
- Spurling's Maneuver
- Transverse Ligament Test
- ULNT - Median
- ULNT - Radial
- ULNT - Ulnar
- Vertebral Artery Test
- Thoracic Spine >
-
Lumbar Spine/Sacroiliac Joint
>
- Active Sit-Up Test
- Alternate Gillet Test
- Crossed Straight Leg Raise Test
- Extensor Endurance Test
- FABER Test
- Fortin's Sign
- Gaenslen Test
- Gillet Test
- Gower's Sign
- Lumbar Quadrant Test
- POSH Test
- Posteroanterior Mobility
- Prone Knee Bend Test
- Prone Instability Test
- Resisted Abduction Test
- Sacral Clearing Test
- Seated Forward Flexion Test
- SIJ Compression/Distraction Test
- Slump Test
- Sphinx Test
- Spine Rotators & Multifidus Test
- Squish Test
- Standing Forward Flexion Test
- Straight Leg Raise Test
- Supine to Long Sit Test
-
Shoulder
>
- Active Compression Test
- Anterior Apprehension
- Biceps Load Test II
- Drop Arm Sign
- External Rotation Lag Sign
- Hawkins-Kennedy Impingement Sign
- Horizontal Adduction Test
- Internal Rotation Lag Sign
- Jobe Test
- Ludington's Test
- Neer Test
- Painful Arc Sign
- Pronated Load Test
- Resisted Supination External Rotation Test
- Speed's Test
- Posterior Apprehension
- Sulcus Sign
- Thoracic Outlet Tests >
- Yergason's Test
- Elbow >
- Wrist/Hand >
- Hip >
- Knee >
- Foot/Ankle >
-
Cervical Spine
>
- I want Financial Freedom
- I want Professional Growth
- I want Clinical Mastery
Expected ECG Findings
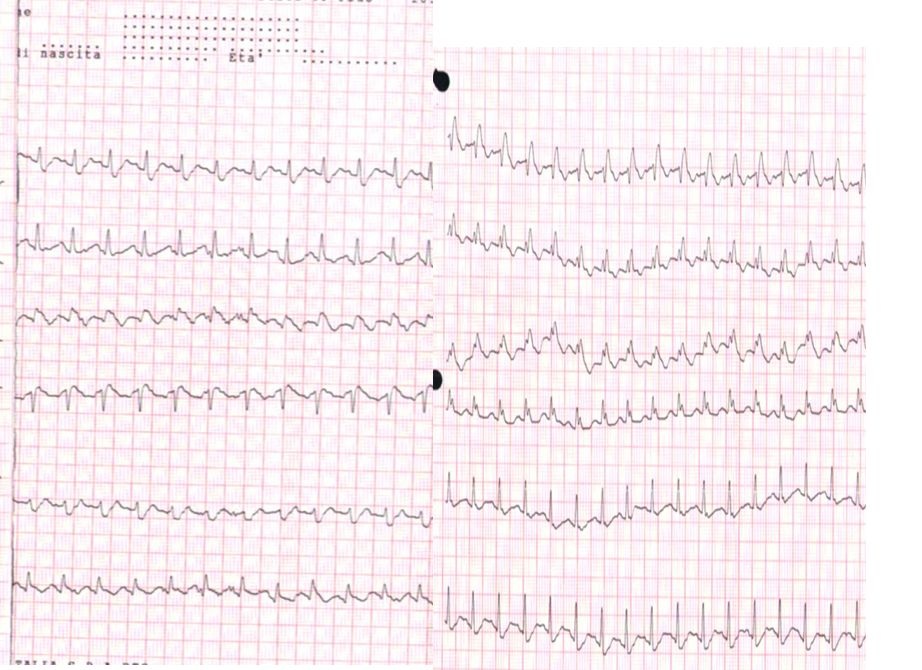
The easiest way to explain the heart rhythm is to refer back to an electrocardiogram (ECG - as depicted below). For review, we will go over the basics of an ECG first: -P Wave: depolarization of atria (starting at the SA node, then spreading out to the atria) -PR Interval: time it takes for the electrical pulse to get from the SA node to the AV node) -QRS Complex: depolarization of ventricles (starting at the AV node; re-polarization of atria hidden here) -T Wave: re-polarization of ventricles This patient in particular, as you recall, had 3 pulses followed by a pause. This likely signifies a Second Degree AV Block: Mobitz Type I (Wenckebach). This would be depicted at a slowly increasing PR interval, before a lack of QRS complex occurs. The cycle then restarts. Basically this means the signal from the SA node to the AV node slows until it doesn't make it through to initiate ventricular contraction, before the next SA node initiates again to restart the cycle. If you've ever struggled with interpretting ECG's, I recommend reading this book by Dale Dubin. It provides a step-by-step understanding and asssessment of ECG's along with the associated pathologies, at an MD level. It is an excellent source for reviewing for a CardioPulm course or preparing for the Cardiovascular section of the boards! -Chris
2 Comments
Kristin
4/28/2014 09:29:34 am
First off--- thank you all very much for being such a positive representation of our field and to the continuation of our education! Your website has been my homepage for over a year now and I love that it keeps me up to date/reminds me of current topics in PT!
Reply
Chad shafer
4/29/2014 11:42:54 pm
Great article about the importance of taking vitals as part of our examination process. Screening is becoming more important, especially in the states that are awaiting direct access!
Reply
Leave a Reply. |
Dr. Brian Schwabe's NEW Book in partner with PaleoHacks!
Learn residency-level content on our
Insider Access pages We value quality PT education & CEU's. Click the MedBridge logo below for TSPT savings!Archives
July 2019
Categories
All
|






 RSS Feed
RSS Feed