- Home
- About Us
- TSPT Academy
- Online Courses
-
Resources
- Newsletter
- Business Minded Sports Physio Podcast
- Day in the Life of a Sports PT
- Residency Corner
-
Special Tests
>
-
Cervical Spine
>
- Alar Ligament Test
- Bakody's Sign
- Cervical Distraction Test
- Cervical Rotation Lateral Flexion Test
- Craniocervical Flexion Test (CCFT)
- Deep Neck Flexor Endurance Test
- Posterior-Anterior Segmental Mobility
- Segmental Mobility
- Sharp-Purser Test
- Spurling's Maneuver
- Transverse Ligament Test
- ULNT - Median
- ULNT - Radial
- ULNT - Ulnar
- Vertebral Artery Test
- Thoracic Spine >
-
Lumbar Spine/Sacroiliac Joint
>
- Active Sit-Up Test
- Alternate Gillet Test
- Crossed Straight Leg Raise Test
- Extensor Endurance Test
- FABER Test
- Fortin's Sign
- Gaenslen Test
- Gillet Test
- Gower's Sign
- Lumbar Quadrant Test
- POSH Test
- Posteroanterior Mobility
- Prone Knee Bend Test
- Prone Instability Test
- Resisted Abduction Test
- Sacral Clearing Test
- Seated Forward Flexion Test
- SIJ Compression/Distraction Test
- Slump Test
- Sphinx Test
- Spine Rotators & Multifidus Test
- Squish Test
- Standing Forward Flexion Test
- Straight Leg Raise Test
- Supine to Long Sit Test
-
Shoulder
>
- Active Compression Test
- Anterior Apprehension
- Biceps Load Test II
- Drop Arm Sign
- External Rotation Lag Sign
- Hawkins-Kennedy Impingement Sign
- Horizontal Adduction Test
- Internal Rotation Lag Sign
- Jobe Test
- Ludington's Test
- Neer Test
- Painful Arc Sign
- Pronated Load Test
- Resisted Supination External Rotation Test
- Speed's Test
- Posterior Apprehension
- Sulcus Sign
- Thoracic Outlet Tests >
- Yergason's Test
- Elbow >
- Wrist/Hand >
- Hip >
- Knee >
- Foot/Ankle >
-
Cervical Spine
>
- I want Financial Freedom
- I want Professional Growth
- I want Clinical Mastery
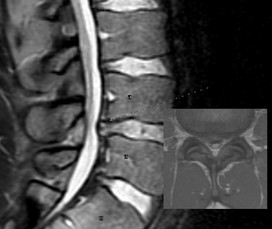 One of the most common pathologies encountered in the health care field is low back pain. It is almost guaranteed that someday in your career as a physical therapist, you will encounter a patient with this diagnosis. With the prevalence of low back pain in our society, there is a large financial drain on the health care system that could be decreased with proper management. The diagnosis of disc herniation as the source of back pain is a controversial issue. There is a large proportion of the population that is asymptomatic and shows disc herniation in MRIs, which leads to the issue of the disc being incorrectly labeled as the source of the patient's complaints sometimes. With the appearance of a herniating disc, some surgeons and patients jump to the conclusion that a surgical procedure is necessary for correction without considering conservative treatment. While surgery can be effective for some individuals, it may represent an expensive overreaction to the patient's symptoms. The study we looked at this week was a systematic review of conservative treatment for lumbar disc herniation with radiculopathy. Studies were only included if the patients were over 18 years old and referred with leg pain (with or without low back pain). 75% of the patients had to have a confirmed lumbar disc herniation through MRI or CT as well. Participants with discs that were only "bulging" were not included. Studies were also excluded if surgery was performed or an injection was used; accupuncture, along with other physical therapy interventions, was labeled as conservative therapy. The review found that advice had poorer short and intermediate outcomes for back pain and leg pain compared to surgical microdiscectomy, but there was no difference in the long term. Those who pursued surgery had better function compared to the advice group at short-term follow-up, but no difference was noted at intermediate and long-term outcomes. Manipulation was found to be effective as long as the annulus was still intact. No difference was found between traction, Low Level Laser Therapy, and ultrasound, but traction had good results when combined with electrotherapy and medications in the short term. The review found moderately strong evidence that stabilization exercises were better than no treatment at all. It should be noted that there are possible adverse effects linked between ibuprofen use and traction. While this article offers some information on the effectiveness of various conservative treatment methods in treating lumbar disc herniation radiculopathy, it does not sufficiently examine the entire scope of physical therapy interventions, such as repeated motions, extension based exercises, neuromuscular education of the core, etc. While there are plenty of studies out there that look at the effectiveness of interventions like repeated motions, neuromuscular education, and core stabilization, there weren't many studies looking at those treatment methods that fit the specific inclusion criteria of this systematic review. It does not mean they are not effective, but it points out an excellent research opportunity for anyone interested. Be sure to keep an eye out for some posts coming out in the near future for treating low back pain. Reference: Hahne AJ, Ford JJ, McMeeken JM. "Conservative management of lumbar disc herniation with associated radiculopathy: a systematic review." Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2010 May 15;35(11):E488-504. Web. 09/15/2012.
5 Comments
8/31/2013 09:03:04 am
Loved your blog layout that I created a weebly account too.
Reply
A couple of days ago i read the conservative treatment for lumbar disc herniation article on you website. By clicking on the link at the end of the article you were redirected to the original review, but when i did so nothing happened (page is no longer found). Therefore, my question; could you send me the review article?
Reply
4/26/2024 04:31:14 am
In treating lumbar disc herniation with radiculopathy, conservative methods are often prioritized before considering surgery. Modalities such as physical therapy, NSAIDs, and epidural steroid injections aim to alleviate pain and improve function. However, in cases of persistent symptoms or neurological deficits, surgical intervention may be necessary. Canada Meds offers a variety of medications to complement conservative treatments, ensuring comprehensive care for patients.
Reply
5/15/2024 04:33:22 am
Conservative treatment for lumbar issues often involves non-invasive methods to manage pain and improve mobility. This approach typically includes physical therapy, chiropractic care, and exercise regimens tailored to strengthen the muscles supporting the lumbar spine. Additionally, lifestyle modifications such as proper posture, ergonomic adjustments, and weight management can play crucial roles in alleviating discomfort. However, recent advancements in medical science have introduced innovative strategies like the Wegovy dosing schedule, which integrates pharmaceutical interventions to address underlying issues. This comprehensive approach aims to optimize patient outcomes by combining traditional therapies with modern pharmacological solutions, offering a holistic approach to lumbar health management.
Reply
Leave a Reply. |
Dr. Brian Schwabe's NEW Book in partner with PaleoHacks!
Learn residency-level content on our
Insider Access pages We value quality PT education & CEU's. Click the MedBridge logo below for TSPT savings!Archives
July 2019
Categories
All
|






 RSS Feed
RSS Feed